1908 Office of the Chief Examiner
(future FBI). ^top^
The Office of the Chief Examiner,
an organization that would later become the Bureau of Investigation
and then the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), is created
by US Attorney General Charles J. Bonaparte. Meant to serve
as the investigative arm of the Department of Justice, the Bureau
of Investigation was initially opposed by Congress, who feared
that its extensive powers could lead to abuse of power. During
and after World War I, the Bureau investigated draft resisters,
violators of the Espionage Act of 1917, and immigrants suspected
of radicalism.
J. Edgar Hoover, a lawyer and
former librarian, joined the Department of Justice in 1917,
and within two years had become special assistant to Attorney
General A. Mitchell Palmer. Deeply anti-radical in his ideology,
Hoover came to the forefront of federal law enforcement during
the so-called "Red Scare" of 1919 to 1920. Hoover set up a card
index system listing every radical leader, organization, and
publication in the United States, and by 1921 had amassed some
450'000 files. More than ten thousand suspected Communists were
also arrested during this period, although the vast majority
of these people were briefly questioned and then released. Although
the attorney general was criticized for abusing his authority
during the so-called "Palmer Raids," Hoover emerged unscathed,
and on 10 May 1924, was appointed acting director of the Bureau
of Investigation.
During the 1920s, with congressional
approval, Director Hoover drastically restructured and expanded
the Bureau. He built the corruption-ridden agency into an efficient
crime-fighting machine, establishing a centralized fingerprint
file, a crime laboratory, and a training school for agents.
In the 1930s, the Bureau of Investigation launched a dramatic
battle against the epidemic of organized crime brought on by
Prohibition. Notorious gangsters such as George "Machine Gun"
Kelly and John Dillinger met their ends looking down the barrels
of Bureau-issued guns, while others, like Louis "Lepke" Buchalter,
the elusive head of Murder, Incorporated, were successfully
investigated and prosecuted by Hoover's "G-men." Hoover, who
had a keen eye for public relations, participated himself in
a number of these widely publicized arrests, and the Federal
Bureau of Investigations, as it was known after 1935, was highly
regarded by Congress and the US public.
With the outbreak of World War
II, Hoover revived his anti-espionage techniques developed during
the first Red Scare, and domestic wiretaps and other electronic
surveillance expanded dramatically. After World War II, Hoover
focused on the threat of radical, especially Communist, subversion.
The FBI compiled files on millions of US citizens suspected
of dissident activity, and Hoover worked closely with the House
Un-American Activities Committee and Senator Joseph McCarthy,
the architect of America's second Red Scare.
In 1956, Hoover initiated COINTELPRO,
a secret counter-intelligence program that initially targeted
the US Communist Party but later was expanded to infiltrate
and disrupt any radical organization in America. During the
1960s, the immense resources of COINTELPRO were used against
dangerous groups such as the Ku Klux Klan, but also against
African-American civil rights organizations and liberal anti-war
organizations. One figure especially targeted was civil rights
leader Martin Luther King, Jr., who endured systematic harassment
from the FBI, including the leaking of sensitive information
gathered by the FBI to his enemies in Memphis, Tennessee, and
elsewhere.
By the time Hoover entered service
under his eighth president in 1969, the media, the public, and
Congress had grown suspicious of the FBI's abuses of authority.
For the first time in his bureaucratic career, Hoover endured
widespread criticism and Congress responded by passing laws
requiring Senate confirmation of future FBI directors and limiting
their tenure to ten years.
On 02 May 1972, with the Watergate
affair about to explode on to the national stage, J. Edgar Hoover
died of heart disease at the age of seventy-seven. The Watergate
affair subsequently revealed that the FBI had illegally protected
President Richard Nixon from investigation, and the agency was
thoroughly investigated by Congress. Revelations of the FBI's
abuses of power and unconstitutional surveillance motivated
Congress and the media to become more vigilant in future monitoring
the FBI.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation
(FBI) is born when US Attorney General Charles Bonaparte orders
a group of newly hired federal investigators to report to Chief
Examiner Stanley W. Finch of the Department of Justice. One
year later, the Office of the Chief Examiner was renamed the
Bureau of Investigation, and in 1935 it became the Federal Bureau
of Investigation.
When the Department of Justice
was created in 1870 to enforce federal law and coordinate judicial
policy, it had no permanent investigators on its staff. At first,
it hired private detectives when it needed federal crimes investigated
and later rented out investigators from other federal agencies,
such as the Secret Service, which was created by the Department
of the Treasury in 1865 to investigate counterfeiting. In the
early part of the 20th century, the attorney general was authorized
to hire a few permanent investigators, and the Office of the
Chief Examiner, which consisted mostly of accountants, was created
to review financial transactions of the federal courts.
Seeking to form an independent
and more efficient investigative arm, in 1908 the Department
of Justice hired 10 former Secret Service employees to join
an expanded Office of the Chief Examiner. The date when these
agents reported to duty — 26 July 1908 — is celebrated as the
genesis of the FBI. By March 1909, the force included 34 agents,
and Attorney General George Wickersham, Bonaparte's successor,
renamed it the Bureau of Investigation.
The federal government used the
bureau as a tool to investigate criminals who evaded prosecution
by passing over state lines, and within a few years the number
of agents had grown to more than 300. The agency was opposed
by some in Congress, who feared that its growing authority could
lead to abuse of power. With the entry of the United States
into World War I in 1917, the bureau was given responsibility
in investigating draft resisters, violators of the Espionage
Act of 1917, and immigrants suspected of radicalism.
Meanwhile, J. Edgar Hoover, a
lawyer and former librarian, joined the Department of Justice
in 1917 and within two years had become special assistant to
Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer. Deeply anti-radical in
his ideology, Hoover came to the forefront of federal law enforcement
during the so-called "Red Scare" of 1919 to 1920. He set up
a card index system listing every radical leader, organization,
and publication in the United States and by 1921 had amassed
some 450'000 files. More than 10'000 suspected communists were
also arrested during this period, but the vast majority of these
people were briefly questioned and then released. Although the
attorney general was criticized for abusing his power during
the so-called "Palmer Raids," Hoover emerged unscathed, and
on 10 May 1924, he was appointed acting director of the Bureau
of Investigation. During the 1920s, with Congress' approval,
Director Hoover drastically restructured and expanded the Bureau
of Investigation. He built the agency into an efficient crime-fighting
machine, establishing a centralized fingerprint file, a crime
laboratory, and a training school for agents. In the 1930s,
the Bureau of Investigation launched a dramatic battle against
the epidemic of organized crime brought on by Prohibition. Notorious
gangsters such as George "Machine Gun" Kelly and John Dillinger
met their ends looking down the barrels of bureau-issued guns,
while others, like Louis "Lepke" Buchalter, the elusive head
of Murder, Inc., were successfully investigated and prosecuted
by Hoover's "G-men." Hoover, who had a keen eye for public relations,
participated in a number of these widely publicized arrests,
and the Federal Bureau of Investigation, as it was known after
1935, became highly regarded by Congress and the US public.
With the outbreak of World War II, Hoover revived the anti-espionage
techniques he had developed during the first Red Scare, and
domestic wiretaps and other electronic surveillance expanded
dramatically.
After World War II, Hoover focused
on the threat of radical, especially communist, subversion.
The FBI compiled files on millions of US citizens suspected
of dissident activity, and Hoover worked closely with the House
Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) and Senator Joseph McCarthy,
the architect of the US's second Red Scare. In 1956, Hoover
initiated COINTELPRO, a secret counterintelligence program that
initially targeted the US Communist Party but later was expanded
to infiltrate and disrupt any radical organization in America.
During the 1960s, the immense resources of COINTELPRO were used
against dangerous groups such as the Ku Klux Klan but also against
African American civil rights organizations and liberal anti-war
organizations. One figure especially targeted was civil rights
leader Martin Luther King, Jr., who endured systematic harassment
from the FBI. By the time Hoover entered service under his eighth
president in 1969, the media, the public, and Congress had grown
suspicious that the FBI might be abusing its authority. For
the first time in his bureaucratic career, Hoover endured widespread
criticism, and Congress responded by passing laws requiring
Senate confirmation of future FBI directors and limiting their
tenure to 10 years. On 02 May 1972, with the Watergate affair
about to explode onto the national stage, J. Edgar Hoover died
of heart disease at the age of 77. The Watergate affair subsequently
revealed that the FBI had illegally protected President Richard
Nixon from investigation, and the agency was thoroughly investigated
by Congress. Revelations of the FBI's abuses of power and unconstitutional
surveillance motivated Congress and the media to become more
vigilant in the future monitoring of the FBI. |
 On
a 26 July:
On
a 26 July: 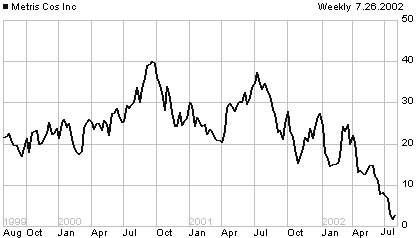 2002
(Friday) The stock of consumer finance company Metris (MXT) rises on
the New York Stock Exchange from its previous close of $1.61 to an intraday
high of $3.00 and closes at $2.85. It had traded as high as $42.56 on
25 September 2000 and $37.05 on 02 August 2001. — In the next trading
session, Monday 29 July 2002, MXT recovers further, to an intraday high
of $4.94, and closes at $4.20. [< 3~year price chart]
2002
(Friday) The stock of consumer finance company Metris (MXT) rises on
the New York Stock Exchange from its previous close of $1.61 to an intraday
high of $3.00 and closes at $2.85. It had traded as high as $42.56 on
25 September 2000 and $37.05 on 02 August 2001. — In the next trading
session, Monday 29 July 2002, MXT recovers further, to an intraday high
of $4.94, and closes at $4.20. [< 3~year price chart] Deaths
Deaths